- What SD-WAN is
- The essence of SD-WAN
- Opportunities provided by SD-WAN
- SD-WAN security: features and privileges
- Conclusion
Today, businesses use cloud services for many procedures - from telephony and accounting to building management. Gartner predicts that by 2021, more than half of the world's companies will have fully migrated to the cloud. According to Cisco AIR, by 2023, the number of Internet users will have grown to 5.3 billion (66% of the population), and the number of connected devices - to 29.3 billion. In such conditions, IT security services for networks come to the fore. We will tell you what the innovative scalable solution SD-WAN is and whether the new technology is able to cope with the set tasks.
What SD-WAN is
In the recent past, the only practice that allowed for the efficient work of users with applications was the deployment of costly MPLS services. The spread of cloud computing has led to the emergence of software-defined technologies. In these technologies, services are separated from underlying hardware and function as a virtual service or system. The SD-WAN technology is one of such solutions.
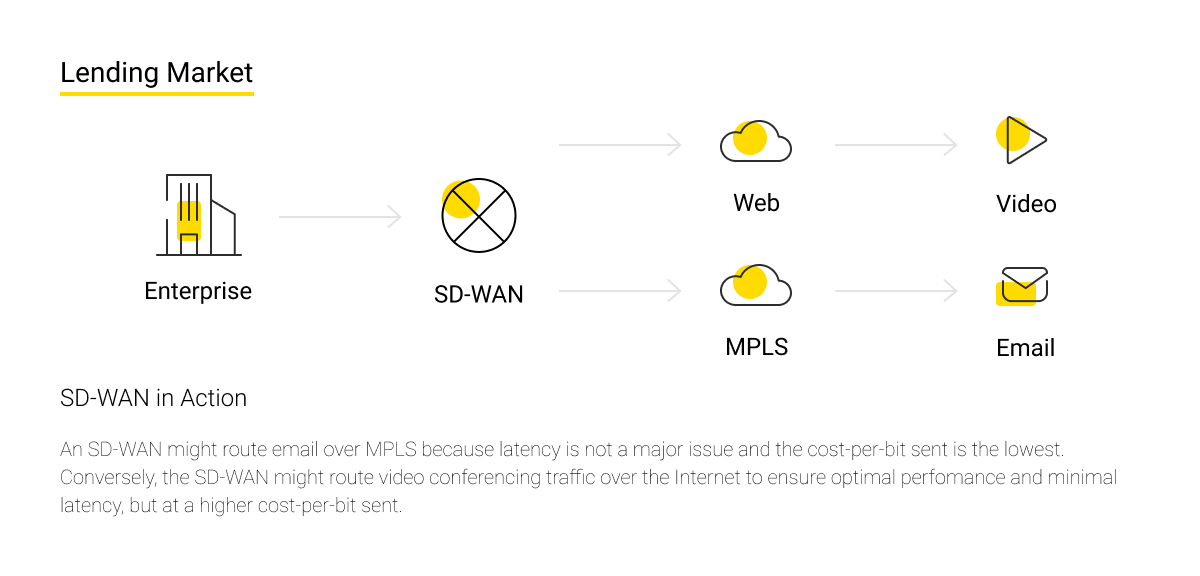
SD-WAN (software-defined networking in a wide area network) is a technology or software that helps to efficiently route traffic based on such factors as priority policy and quality of service (QoS) settings.
SD-WAN allows companies to use any combination of transport services, including MPLS (a protocol for accelerating and forming network traffic flows by data priority), LTE (a standard for wireless high-speed data transmission), broadband Internet access, cellular network, and a satellite for secure use of applications.
What's the main difference between the new technology and the already established router-based WAN structure? The SD-WAN solution is designed to fully support and deliver software hosted in data processing centers (DPCs), public or private clouds, and SaaS platforms (Salesforce.com, Workday, Office 365, and Dropbox).
With the help of SD-WAN, centralized management of secure and efficient routing of traffic through the broadband network is carried out. This increases software performance and improves the quality of interaction with the user. Thus, the new solution increases the productivity and flexibility of a business and reduces its IT costs.
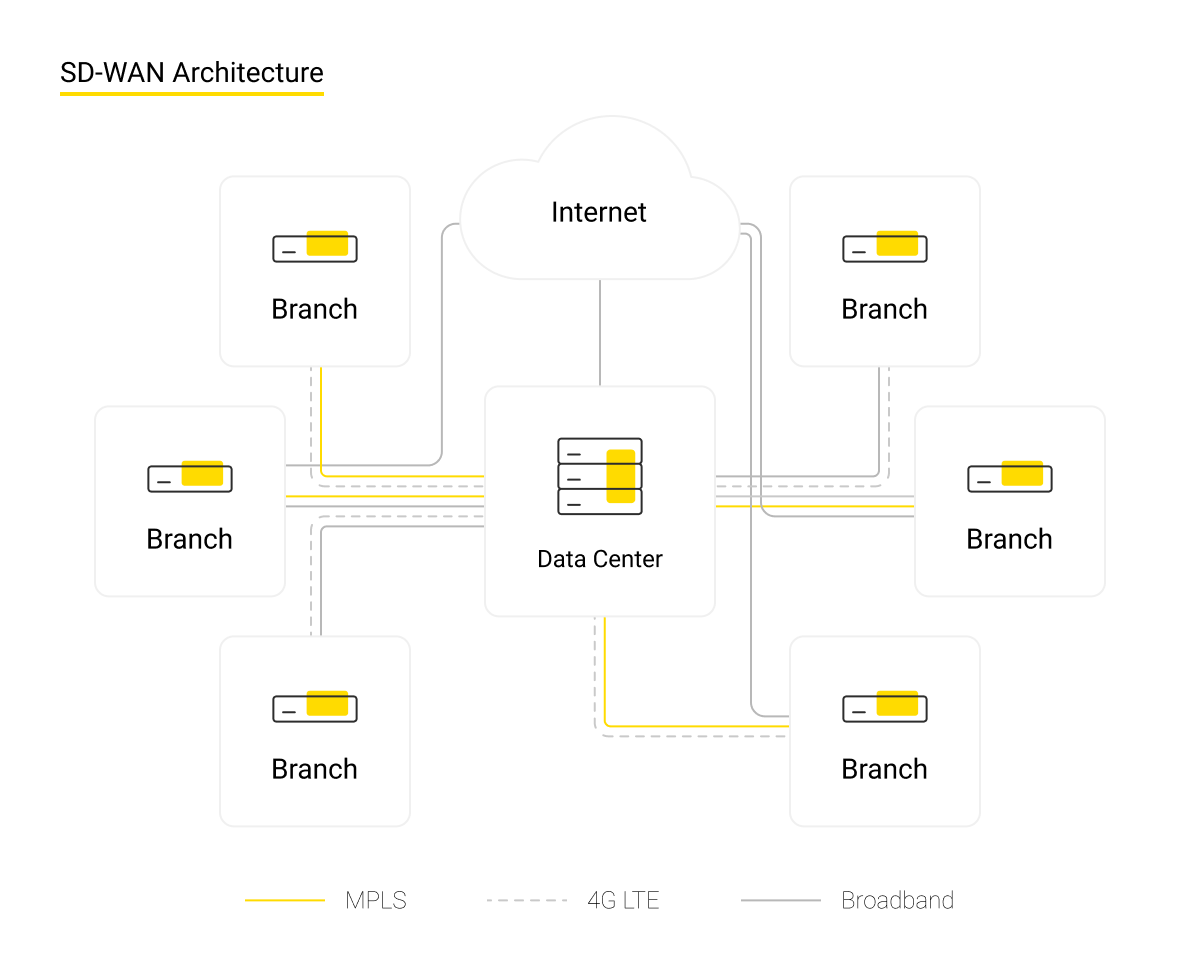
The essence of SD-WAN
A typical telecommunications infrastructure of an organization is built as follows. There is a head office and branches that require creating a common information space without losing the quality and reliability of data transmission. The company buys a communication link from a telecommunication provider, the cost of which exceeds the price of a regular Internet connection. Next, the customer needs to create their own telecommunications network that includes routers, network devices, and firewalls, and then configure it.
However, if a company plans to open a branch in an area that is not served by the telecom operator, there may be problems. For example, the launch of a new office will be delayed or costly. In such situations, the connection problem can be solved in non-standard ways: by laying optical fiber at best and by using an LTE modem at worst.
These difficulties can be eliminated far more easily - by using the SD-WAN technology. Special software is installed on the controller of the head office’s DPC, which establishes and controls the operation of the software-defined WAN. Less “smart” low-cost switches in the branches connect to the host computer's controller.
Thus, there is no need to send a specialist to a newly-opened branch - any employee can cope with the task. Send a router, insert a SIM card or a patching cord, plug it into an outlet - and the job is done.
Opportunities provided by SD-WAN
SD-WAN processes traffic by order of importance, QoS, and security according to the needs of a business. This technology can leverage physical, virtual, and cloud devices for consistent centralized management of app policies and threads across all branches of WAN.
SD-WAN widens a company's opportunities in the following ways:
- Allows firms to monitor and efficiently distribute traffic.
By acquiring an SD-WAN solution, the customer doesn’t need to develop and maintain a concurrent monitoring system. Typically, the controlling system of SD-WAN includes solid monitoring functionality. Vendors offer ready-made techniques for managing device configuration, which simplifies the routine tasks of network administrators.
Let's say a branch has direct access to the Internet and a channel dedicated by a provider. The router constantly checks the quality of all available channels, which makes it possible to organize application traffic routing, taking into account service level agreement (SLA). For example, voice traffic goes through LPS, and then the delay on the provider's network increases. The SD-WAN Controller will automatically transfer the voice traffic to the channel with the required SLA. Thus, it is possible to distribute program traffic through the type of channel that is currently optimal.
- Improves the quality of data transmission.
The SD-WAN solution helps to measure the quality of channels and offload some of the traffic to the required Internet channel. If the channel degrades so much that even an non-critical application works poorly through it, it is possible to return the program to a high-quality channel currently producing the SLA that the program needs.
Special protocols - PD and FEC - help to fight losses on low-quality channels. For example, with PD, it is possible to transmit the same data over two channels. And if you have lost a packet via one channel, it can be easily restored via the other. The router on the receiving side eliminates this duplication and forwards the information further to the local branch network.
FEC is some additional information that is transmitted for a certain number of packets and some hash. If we have lost one of the packets but have a hash, we can restore this packet. These may be transactions that don’t require a lot of bandwidth, but they must have been successfully transmitted at the first attempt.
For example, a customer pays for goods at the checkout, and kilobytes of data are generated there, which need to reach the DPC of a retailer. This is important because otherwise the terminal may show an error, and a disgruntled queue will gather at the checkout. Thus, we don't lose anything in terms of bandwidth consumption and improve customer experience.
- Provides fast introduction of new servers.
In order to connect routers at branch offices, we don’t need to have an IT specialist on-site. Any employee is able to puzzle out the instructions for connecting a device. Then, the device automatically connects to the main server, receives the necessary configurations, configures itself, and the branch joins the company's secure network. This procedure significantly saves an organization's time and resources.
- Reduces IT costs.
Connecting MPLS is much more expensive than broadband Internet, mobile, or satellite connectivity plans. The connection procedure itself and other operations associated with transferring, adding, and changing branches create significant overhead costs. Outdated security models also mean that the likelihood of data breaches can increase over time.
SD-WAN links several network transport modes for real-time application transmission and consolidates their bandwidth. Any organization has the right to improve expensive contracts with telecom operators, cut the number of equipment in offices, and manage branches via a common interface - quickly and at a lower cost.
For example, Entegra Bank, a fast-growing financial institution in North Carolina, has switched from MPLS to SD-WAN broadband at its 22 branches. As a result, costs for WAN connectivity have reduced by 50%, while bandwidth has increased on average by five times.
SD-WAN security: features and privileges
Business owners are often concerned that transforming corporate WANs and branch networks into an SD-WAN will create vulnerabilities to threats and additional security challenges.
Many present-day security architectures operate based on combining data flows at the stage of traffic transmission through a centralized “channel” to a DPC. By using traditional firewalls on the premises, organizations create a single point to check the security of packets before they reach the DPC. This traffic filtering method doesn’t work in SD-WAN architecture.
SD-WAN security is primarily based on the use of IP security (IPsec), VPN tunnels, next-generation firewalls (NGFW), and micro-segmentation of application traffic. Network administrators coordinate these security elements on a centralized basis by using software that provides a detailed overview of the network.
Hamza Seqqat, Director of Solution Architecture at Apcela, outlines four advantages of SD-WAN security:
- Handling VPN problems.
Before SD-WAN, companies built VPN or DMVPN to provide resilient transport of their traffic. But for this purpose, they had to install firewalls in their DPCs and VPN devices or firewalls in branch offices to run these VPNs.
When using SD-WAN, you needn’t worry about building your own VPNs or encrypting your traffic. The Controller does this automatically. A user only needs to give an IP address to the device or enable DHCP and let it select an IP address from a DHCP server.
The SD-WAN Controller builds a full mesh so it can communicate with each website without going back to the DPC. Traffic between websites becomes secure, easy, and smooth. SD-WAN uses encryption and a VPN to protect traffic that is sent over a public Internet connection.
- Reducing traffic that goes through the security system.
Security management also becomes easier because SD-WAN reduces the amount of traffic that goes through the security parameters.
Without SD-WAN, you usually have to pass the whole gig through a firewall that sends some of the traffic to the DPC and some of it to the Internet. In SD-WAN, traffic is segmented using a split tunnel so that half of the traffic can be taken and pushed through the firewall to go to the Internet. The other half will go straight from one website to another, without having to go through a security parameter.
This is of paramount significance because most security products are based on bandwidth and usage. Traffic from different applications travels through separate SD-WAN micro-segments, so an outside threat can’t compromise all application traffic.
- Ensuring security during initial deployment.
SD-WAN has some built-in security capabilities. This technology is able to allow and deny certain websites and restrict traffic going to particular websites.
Due to its encrypted traffic capability, SD-WAN is by default secure during initial deployment. The protection mechanism - authentication - is usually based on the presentation of certificates: the device checks what it connects to, and the control component checks what is going to connect to it. The high visibility of SD-WAN helps administrators maintain network security as they are able to see in detail where the vulnerable point is.
A global survey of IT specialists by Vanson Bourne showed that a third of employees have already deployed SD-WAN at most of their sites, and 49% are in the process. More than a third of organizations (36%) have connected a clean SD-WAN that required additional security - a firewall. However, 30% of SD-WAN users said that later on, they would prefer a single solution that includes security.
- Using security platforms.
SD-WAN suppliers have made great progress in partnerships with cloud security providers and cloud service importers. When providing traffic encryption and security over SD-WAN, security platforms only deal with public Internet traffic. Some SD-WAN products automatically route all traffic through security platforms that define cloud-based security parameters before it reaches the Internet or cloud services providers.
Cloud-built secure web gateway protection scans and filters SD-WAN traffic for malware, botnets, and other web threats, no matter where the user is or how their traffic is routed. Built-in on-premises and cloud security tools enable IT divisions to prevent threats anywhere - from branch offices using cloud-based SaaS or IaaS services to DPSs and the global Internet.
Conclusion
The right and reliable SD-WAN solution helps to tackle many of the complex cyber security services issues that organizations face when using public networks for sensitive workloads. With this new secure technology, highly secure hybrid networks can be deployed.
SD-WAN is gaining increasing popularity in cyber security assessment services. Companies need fast, scalable, and reliable connections between branches - at the lowest cost and the best quality. Contact us if you need a hand with properly implemented SD-WAN that will ensure superior security of your software providing you with a high-performance, resilient, and cost-effective WAN.







