- What is a neobank and how does it work?
- Neobanks, digital banks, and traditional banks - what’s the difference?
- Key benefits of neobanking
- Challenges of building a neobank
- Developing a neobank from scratch: steps and core features
- The discovery phase
- Elaborating the design
- Creating an MVP
- Testing, deployment, and maintenance
- Conclusion
Today, making a transaction by simply swiping across the screen of a mobile device is becoming the new normal. As technology excels, both market behemoths and fintech startups must consider leveraging artificial intelligence, cryptocurrency payments, blockchains, and other achievements of the digital era to gain a competitive edge. One of such novelties is digital-only banks. Having been around for the last fifteen years, they are now gaining momentum as more and more clients take for gra nted the ability to make instant, fee-free, multicurrency, and highly secure transactions. What is their role in the financial landscape, what products do they offer, and is it worth founding one? Read on for our professionals’ opinion.
What is a neobank and how does it work?
The banks that most of us are used to are physical branches with ever-busy clerks and heaps of documents. Yet some functions of these old-fashioned institutions have increasingly been taken over by companies that have, in fact, nothing to do with banks.
The neobank definition includes digital-only initiatives launched by non-bank companies. They make it possible to perform some of the habitual banking operations in no time and free of cost via dedicated platforms.
How exactly does this work? The companies providing such services get their revenue mainly through establishing substantial interchange fees, charging their clients for using third-party ATMs, and seeking funding from investors who sometimes represent large financial institutions. To be able to operate, they either apply for a banking license or collaborate with regulatory-compliant banks, or else avail themselves of both the above options.
Some outstanding examples of national and international neobanks include the South Korean Kakao Bank, the Chinese WeBank, the US Chime, the well-known UK-based Revolut, the German-based N26, the Spanish Bnext, and the world’s highest valued establishment of this kind as of 2021, the Brazilian Nubank.
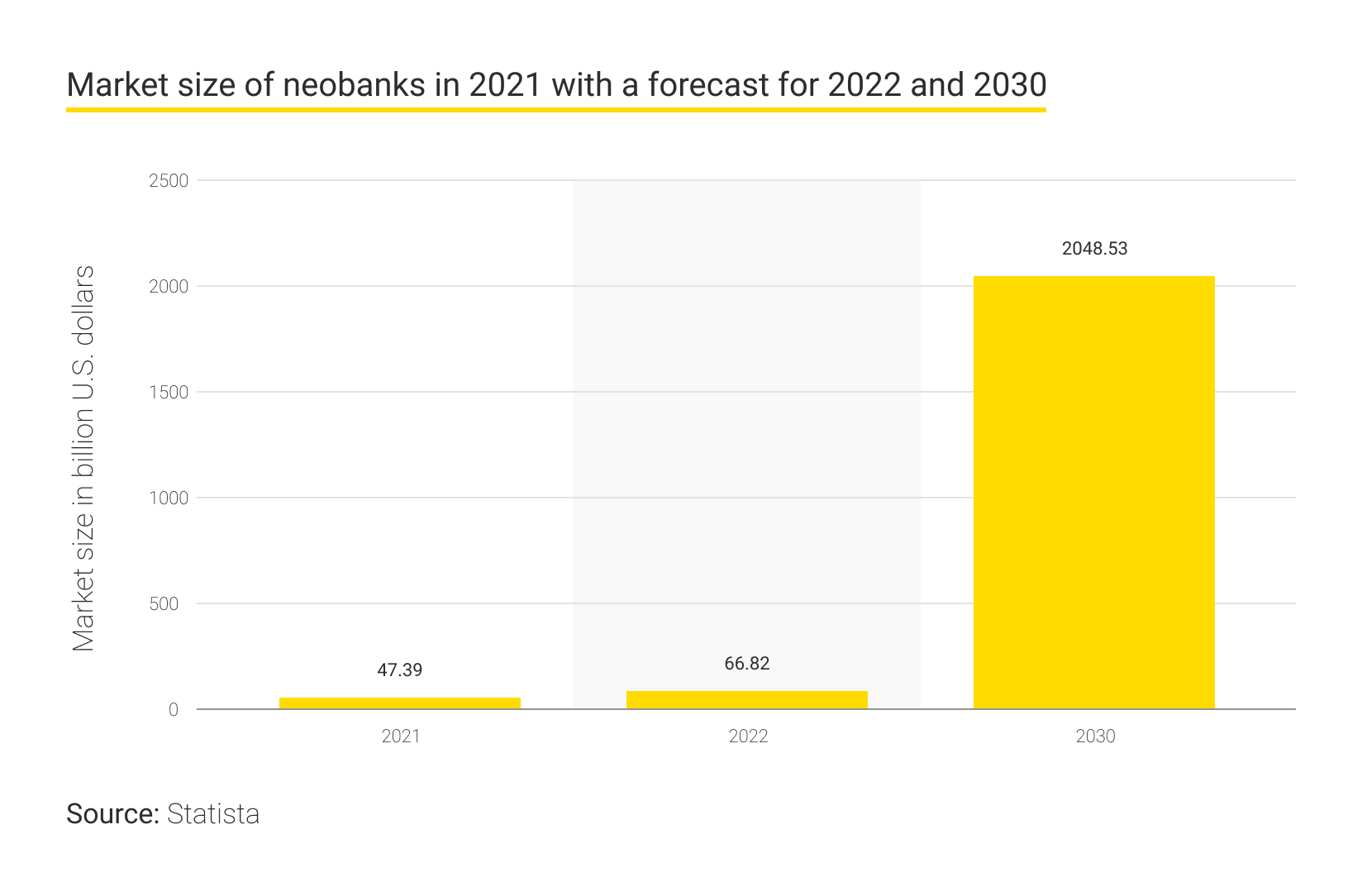
The size of the neobank market is growing at an incredible pace of 53.4% yearly, amounting to $47 billion as of last year. By 2025, these companies are predicted to serve around eighty million clients in the US alone, while the number of current clients globally exceeds a billion. In total, there are approximately four hundred digital-only banks worldwide, with the biggest neobanks concentrated in North America, the UK, Brazil, South Korea, and Sweden.
Neobanks, digital banks, and traditional banks - what’s the difference?
To join the globally popular trend, decision-makers must not only understand the neobank meaning but also know how it’s different from online banking and traditional institutions.
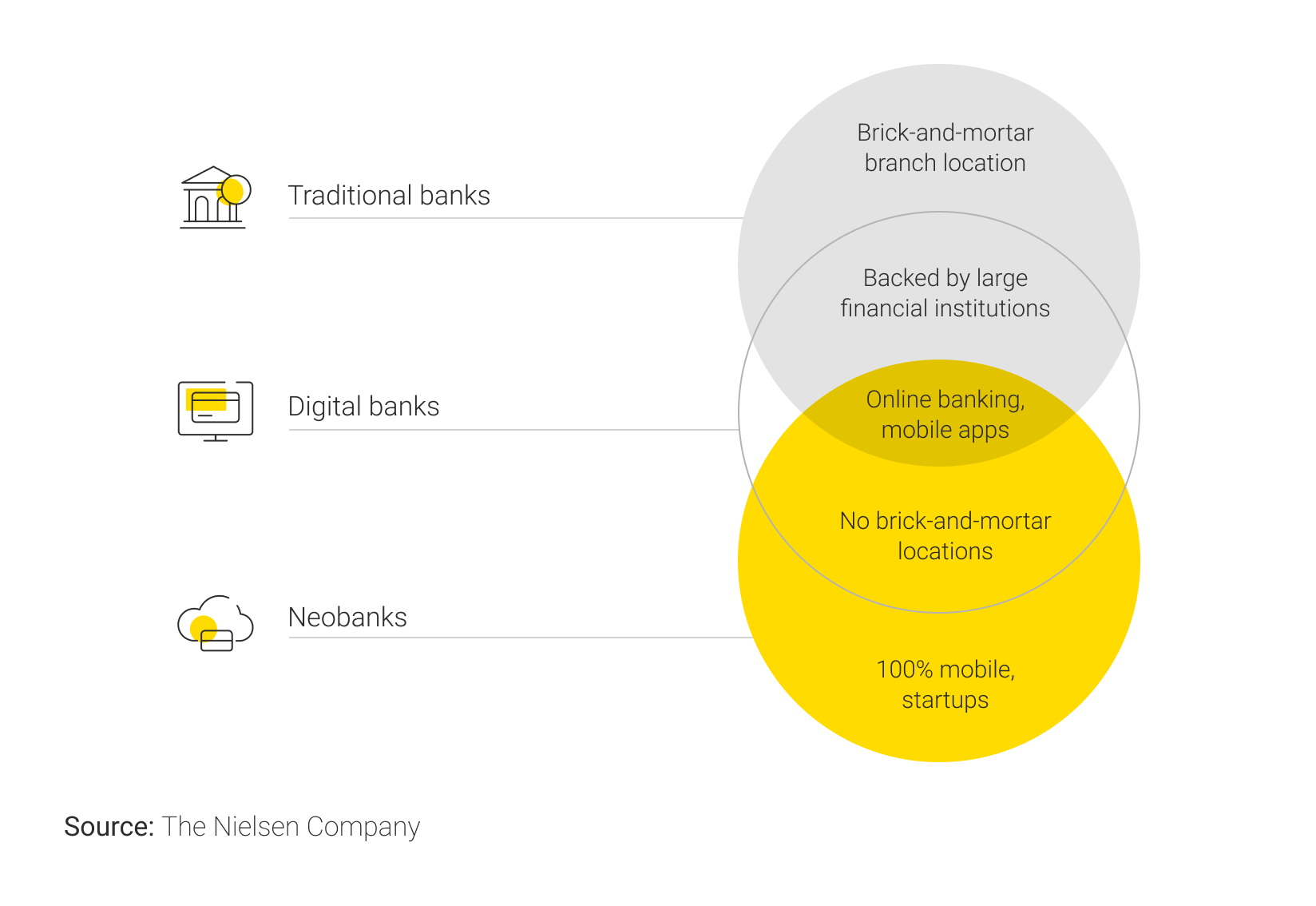
The above concepts overlap as traditional and online banks increasingly exploit novel technology. Below is a brief explanation of each of these phenomena:
- Brick-and-mortar banks operate under a banking license and are backed by major financial institutions. They provide diverse services such as the issuance of mortgages, loans, the opening of savings and checking accounts, and more, typically charging for them at a higher rate than the other types of banks. Although these establishments offer high reliability and a personalized approach, they lack the flexibility to adapt to the changing reality, as well as the accessibility to make their services available at any time and from any location.
- Digital banks are conventional financial establishments operating under a license and serving their clients via apps and platforms. They provide seamless access to habitual services, e.g. opening bank accounts, taking on loans, making payments, etc. Along with that, clients can choose between in-person and online assistance, which comes in handy when the need to solve complex issues arises.
- Digital-only banks, aka neobanks, have neither physical locations nor their own ATMs, necessitating that their clients use those of their partners and third-party banks. They are not bound by all the regulatory regulations that are mandatory for their traditional counterparts. This makes them more flexible to adopt novelties and innovations such as cryptocurrency payments, crowdfunding and robo-advisor features, NFTs, and so on. However, they usually offer a limited range of basic products such as savings accounts, debit cards with no ATM fees, mobile check deposits, etc.
It’s worth mentioning that the biggest neobanks had an invaluable impact on the development of the entire industry, raising financial service standards in the digital era. These novel companies encouraged competition across businesses, pushing them towards innovativeness and enhanced product quality.
Key benefits of neobanking
Upon answering the question “What is neobanking?” business owners might want to know how exactly these startups are profitable. Andersen’s experts identified the following key points:
- Affordability. Since all the company-client interactions take place online, the companies save on maintaining branch offices and therefore, can offer high interest rates and products at favorable prices. This makes their services affordable to a large number of people.
- Convenience. The clients can manage their accounts at any time, from any part of the globe, and from the device of their preference. In addition, they can enjoy the high-tech nature of products with embedded AI algorithms and enhanced possibilities.
- Flexibility. Digital-only banks are far less bound by industry laws than traditional establishments. Therefore, they have more space for experimenting and inventing novel products that meet the demands of their tech-savvy clients.
- Quick start. Because of less strict formalities in the procedure for starting a business, they can be launched expeditiously and start bringing return on investments sooner. Some countries, e.g. Australia and the UK, have a special license for such startups, empowering them to operate in the market even before they obtain a full-fledged license.
Challenges of building a neobank
The stakeholders who look at the success of the biggest neobanks should nevertheless understand the following risks that these businesses imply:
- The inability to launch certain products on their own. This follows from the fact that these startups are not full-scale financial institutions with operations backed by a charter and a full range of regulations. To avail themselves of certain services, e.g. opening a deposit account, clients would need to choose the digital-only banks that are supported by a licensed bank.
- The absence of in-branch service. The companies must ensure clear and intuitive interfaces for clients to navigate their solutions as, due to the lack of physical branches, they won’t be able to solve their issues in person.
- The need to take industry regulations into account. The laws that govern the operation of financial institutions vary from country to country. Startup owners must attentively study the requirements they have to comply with, e.g. the e-money institution licensing, the General Data Protection Regulation, the EU Directive on Payment services (PSD 2), the Know Your Customer standard, etc. Introducing the role of a compliance advisor can help companies in fulfilling this challenging task.
- The lack of niche-specific expertise. Not every fintech expert knows how to start a neobank as they haven’t been around for many years. Andersen recommends business owners turn to reliable finance software development companies that are able to provide solid niche and technical expertise.
Developing a neobank from scratch: steps and core features
Before embarking on the development of their digital product, shareholders should find the answers to the following questions:
- What products and services will their company offer?
- Where to seek funding and what institutions to partner with?
- How to ensure ATM coverage?
- What service fees and interest rates are reasonable for the clients?
- Is there a robust risk management system in place?
- Is there a trusted fintech software development company to provide an advanced technological solution?
Once signing a contract with a reliable vendor, the business owners will entrust them with the following project stages.
The discovery phase
Seasoned business analysts will go through the neobank definition, elicit and prioritize business and technical requirements, study the examples of international neobanks that are likely to compete with the startup, and outline user personas. After evaluating the business idea’s feasibility, the specialists will draw up the documents needed for further stages, e.g. the Vision and Scope document, the roadmap, the Architecture Vision, etc.
Elaborating the design
On the basis of product requirements, professional UI/UX designers and IT architects build the software logic and create prototypes to envision the customer journey. Thus, the developers will be able to bring the product idea to life by following the clear plan and detailed specifications.
Creating an MVP
This stage is recommended for complex digital-only banks to test the solution’s essential functionality before the creation of a full-scale product. These features include:
- Clear and secure authorization process, including biometric data verification and two-factor identification;
- In-app guidance with tips on how to make the most out of the solution’s features;
- Seamless payments and transfers, including the creation of templates, using various currencies and payment options, viewing the transaction history, and benefiting from making fee-free cross-border transfers;
- Instant notifications to inform the users of their account activities and app updates;
- Card issuance, including virtual and physical cards and those with cashback offers;
- Dynamically changing CVV2 for enhanced transaction security;
- Loan services, savings accounts, and other products.
Testing, deployment, and maintenance
At this final stage, the app is tested end-to-end to deliver a high-quality product to the users. After its launch, the vendor’s specialists collect analytics to improve it in the subsequent releases. They also maintain it to guarantee its seamless performance throughout the entire life cycle.
Conclusion
Digital-only banks emerged as a novel solution to the challenges of today’s increasingly digitized world. Although these ground-breaking fintech companies are unlikely to overtake legacy institutions, they will, according to forecasts, continue to develop at a dizzying pace and further transform the industry. If you are wondering how to start a neobank that will generate a steady income, turn to Andersen for a free consultation. Our fintech software development experts have successfully completed dozens of custom projects and will be happy to give you a hand with your finance app development initiative.