- Digitalization in logistics. A brief assessment
- Some practical motives behind logistics digitalization
- Digital development areas in logistics
- Digital technologies in logistics
- Examples of what Andersen could build for you
- Final remarks
The economy has turned into a thoroughly digitized space. Companies in multiple fields constantly introduce fresh innovations to match evolving market demands and withstand the ever-present dynamic competition. Understandably, the logistics industry is also aspiring to integrate digital tools applied to handle orders, vehicles, warehouses, inventories, etc. As many as 70% of all the enterprises in logistics have already undergone a certain degree of digital transformation.
Let’s take a glance at what technologies underpin digitalization and why it is worth investing in custom logistics software development.
Digitalization in logistics. A brief assessment
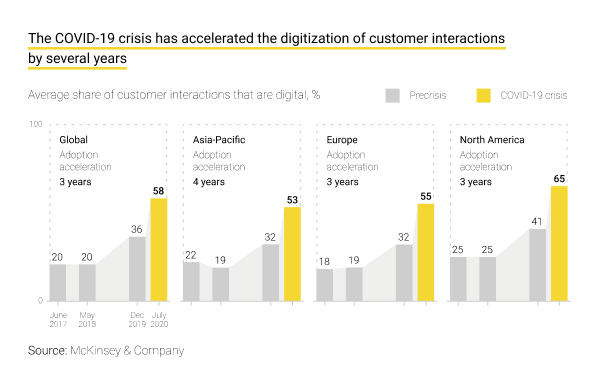
Since 2020, digital transformation in logistics has been boosted, first, by the pandemic and then, second, by large-scale armed conflicts, political tensions, sanctions, and trade restrictions. Initially, the logistics companies had to suffer from transportation cancellations, social distancing policies, and strict quarantines all over the globe. It took them some time to adapt to the new working conditions and update the rules for employees, respective routes, supply chain visibility and control methods, etc. Then, right after the public health crisis, we entered a new global era of costly uncertainty, which also contributed to digital transformation in the logistics industry.
Nothing illustrates this successful struggle against all odds better than this graph from Statista. Back in 2020, we observe a totally predictable slump. Then, a stage of recovery ensues. However, logistics operations are getting revived unevenly, note the illustrative results of 2023. Still, the future, according to expert-level forecasts, looks bright for the logistics industry.
For sure, this hallmark of resilience and preparedness to grow despite all the new challenges cannot be explained without the powerful factor of digital transformation in the logistics industry. Indeed, business executives report that Covid-19 has accelerated the digital transformation in logistics by an average of 5.3 years. Subsequent negative developments for the world economy we have already mentioned, and their consequences for logistics processes, supported the technological progress.
It quickly became crystal-clear: if any given cargo company continues doing business using traditional outdated ways, it will lose its competitiveness and value. Hence, all are investing into digital tools for logistics processes now. Available industry-specific figures speak for themselves:
- The 2020 baseline for digital transformation spending in logistics was ‘only’ $3 billion;
- As for 2023 estimates, they are fluctuating around $60 billion;
- Expectations from 2030 exceed $120 billion.
In these circumstances, it is, beyond doubt, worth investing in custom logistics software development, as long as your company wants to stay competitive in the new logistics 4.0 world, defined by such properties as interconnectedness, intelligent automation, total traceability, smart warehousing, and sustainability.
Some practical motives behind logistics digitalization
Speaking of narrower, easily calculable, and tangible considerations, with the aid of digitalization in logistics, market players are addressing the following pressing issues:
- Cut fuel price tags
Fuel is a large expense item. Price increase incurs losses if the organization doesn’t manage to raise shipping costs in time. Given the unpredictable nature of the oil market, logistics companies must develop contingency plans for the purposes of maintaining profitability and preventing potential disruptions.
- Streamline corporate flows and processes
Organizations are aspiring to optimize supply chain operations:
- Manage the shipment of their goods promptly and accurately so that no truck leaves half empty.
- Manage their fleets more efficiently in order to offer profitable routes and save gasoline.
- Monitor their warehouse inventories in order to place products more compactly and send them for shipment faster.
Digital solutions for logistics - systems for managing orders, vehicles, inventory, and storage - are created for the above purposes. With such solutions, it is easier to reduce fuel and maintenance costs, satisfy client needs, increase profits, and make a business more efficient.
- Enhance the customer experience
Speaking about eCommerce, consumer demands are rising significantly. Statistics say that 40% of buyers are satisfied with receiving their orders within two days, 18% expect delivery within a day, while the remaining customers are willing to wait three to four days for their products.
An enterprise can swiftly deliver products if their working mechanisms go like clockwork and there are no delays in the delivery of goods to the warehouse, in sending them to the client, and so on. This can be achieved through business digitalization, where every element of the supply chain is controlled.
- Overcoming the driver shortage
A lack of professional drivers hinders the advancement of the sector. Usually, young candidates are unwilling to put up with the working conditions. The IRU report states that the deficit of specialists in the examined countries accounts for 7% of unfilled positions. Continuous travel and a lack of sleep are only some of the factors why young people feel explicitly reluctant to become truck drivers. The industry mainly hinges on men who are 45 years old or older.
The mentioned problems can be partially solved through custom logistics software development.
Digital development areas in logistics
Digital transformation means the introduction of programs, robots, and devices (drones, sensors, etc.) into the activities of a company. Enterprises develop internal operations in the following three directions:
- Hyper automation.
Firms combine several technologies to improve their processes and interactions between suppliers, customers, the purchasing department, drivers, etc. For example, AI and Optical Character Recognition handle unstructured sales orders. To attain greater efficiency, Robotic Process Automation is connected to this model so that an operation is carried out without human intervention.
- Elastic logistics.
Flexibility allows organizations to adapt to the market demands and either reduce or expand their supply chains. It solves the problems of slack loads, small storage areas, goods lying for too long, and other inefficiency issues. Elastic logistics is based on Big Data analysis and AI and ML algorithms.
- Greener logistics.
Sustainable logistics focuses on minimizing environmental harm throughout transportation, warehousing, and related operations. It strives to align the activities of freight companies with goals that support economic growth, environmental preservation, and societal well-being. Green supporters want to:
- improve fleet management in order to plan the route and loading of goods more efficiently;
- automate warehouse management to save energy and resources;
- optimize inventory control through robotization.
How do these areas get implemented in real life?
Digital technologies in logistics
In order to solve the industry problems through hyper automation, elastic, or green logistics, digital transformation requires the properly matching technologies. Among the participants of a survey by Logistics Viewpoints, 80% noted that they need innovations as never before to enhance transparency and reliability.
Digitalization is determined by the following innovations:
- Internet of Things
Real-time data exchange flows, fueled via IoT sensors, promise 100% real-time visibility of the supply chain. Via this technology, carriers are able to more effectively control their fleets and technical condition of vehicles, as well as track shipments and cargo deliveries.
Also, the IoT allows cargo shippers to have better control over the storage conditions of their cargo, its placement on the site, and transportation. Internal processes enhanced with the help of the IoT save both parties their time, fuel, money, and reputation. Concerning the current adoption rates, we are already living in an IoT-word. Per the recent State of AI Adoption survey, 55% of logistics companies utilize between 1,000 and 10,000 IoT devices, while 38% operate smaller networks of 500 to 1,000 devices.
- Cloud computing
In the early 2020s, the Accenture Technology Vision 2021 research found that cloud computing was a priority for 42% of supply chain managers, and 93% of the survey respondents were confident that more than 50% of logistics businesses would go to the cloud within the next three years.
The cloud gives logistics the flexibility and scalability it lacks - companies are able to increase or decrease the scope of work based on demands. This technology helps in implementing the ideas of environmental sustainability. Applications with cloud architecture can reduce harmful gas emissions by 5-10%.
Along with that, the cloud makes Big Data analytics and collection easier. Such analytics are needed to adjust corporate strategies and do business more efficiently.
- AI/ML
ML and AI algorithms reveal fresh possibilities for the logistics - from autonomous vehicles to Predictive Analytics. McKinsey has found that these technologies are mainly used for the following four business functions:
- service delivery;
- product and service creation;
- marketing;
- supply chain management.
Around 2020, there were as little as 12% of supply chain professionals relying on AI. As of 2023, the adoption rate among key logistics companies hit 27%, and the trend continues. Those who manage to integrate AI win. Among other things, per McKinsey, early adopters of AI-driven supply chain approaches have achieved significant gains, diminishing logistics costs by 15%, cutting inventory levels by 35%, and elevating service levels by 65%—outpacing competitors who have been slower to adapt.
- Robotic Process Automation (aka RPA)
The logistics sector is gradually introducing the following types of automation:
- Automated guided carts;
- Autonomous mobile robots (AMR);
- Drones;
- Autonomous cars;
- Driverless trucks;
- Forklifts, etc.
AMRs move along predetermined routes, transporting goods for dispatch and storage. Drones accurately count inventory and enter the information into the inventory management system.
Driverless cars and trucks are a part of the long-term perspective, although Kodiak Robotics plans to launch a fourth-generation autonomous truck later this year. They are striving to organize long-distance cargo transportation without people by 2023. Smart transport will solve the problem of driver shortages and reduce the number of accidents.
Experts suppose that driverless vehicles will cut transportation costs, optimize fuel consumption, and shorten delivery timeframes. McKinsey predicts savings of 45% ($85 billion to $125 billion) for the US market.
- Digital twins
Through this technology, tech specialists design a virtual copy of a real object or process. Logistics firms create 3D models of warehouses to experiment with their planning - determine how to place inventory on the site so that it can be quickly found and loaded into vehicles later.
For example, Ericsson and the port of Livorno in Italy are designing a digital twin that will help to ship goods faster. They are building a digital analog of the port area using the 5G network, IoT sensors, LiDAR, and cameras.
Digital twins can monitor product storage conditions, vehicle technical states, and driving behavior, as well as optimize other operations pertaining to the supply chain.
Benefits of digital transformation in logistics
Digitalization is fundamentally changing the way a logistics business is run and gives it a number of advantages:
- High speed. Streamlining and real-time control help to avoid delays in warehousing activities and during cargo delivery.
- Cost-efficiency. When a particular firm exercises dependable control over gasoline costs, uses mobile robots, or knows how many items to order per season, it saves valuable resources.
- Loyal clients. The sooner consumers receive their orders, the better they think of the supplier. Tracking cargo trips is the new standard that customers love.
Examples of what Andersen could build for you
Regarding digital tools for logistics operations and transformation, Andersen is fully prepared to become your trusted vendor of custom software development. The range of projects we could assume responsibility for includes, but not limited to:
1. Predictive analytics software. Harness big data and advanced algorithms for demand forecasting, inventory management, and predictive maintenance. Optimize stock levels and prevent potential failures using actionable insights from rich data streams.
2. IoT and telematics systems. Enhance shipment tracking and asset monitoring with real-time sensor data. IoT-enabled solutions provide precise visibility and connectivity, eliminating operational blind spots.
3. Fleet management suites. Centralize and automate fleet operations with tools for smart scheduling, driver risk reduction, and real-time tracking to maximize efficiency and safety.
4. Supply chain management platforms. Streamline fragmented supply chains with unified systems. Gain full visibility into inventory, order tracking, and warehousing activities, enabling seamless collaboration among stakeholders.
5. Cloud computing basis for digital transformation. Guarantee flexibility, scalability, and secure remote access. Cloud-based infrastructure supports agile operations and digital transformation for logistics entities.
6. Blockchain applications. Build trust and lucidity in supply chain transactions. Immutable ledgers record shipment details, reduce fraud, simplify audits, and resolve disputes efficiently.
7. AI-Powered logistics tools. Leverage AI for smarter route planning, operational optimization, and predictive analytics. Minimize inefficiencies and enhance client satisfaction with data-driven decisions.
7. Mobility-as-a-Service Platforms (MaaS). Integrate transportation services into unified applications for on-demand mobility. Encourage eco-friendly transit and reduce the reliance on personal vehicles.
8. Demand planning systems. Predict logistics capacity needs using AI-driven tools that assess historical data and market trends. Optimize resource allocation practices and get adjusted to fluctuating demand seamlessly.
9. Digital tools for last-mile delivery operations Automate and refine the final stage of delivery with technologies like self-driving vehicles, drones, and integrated customer feedback systems for enhanced speed and satisfaction.
Final remarks
Digital transformation is radically changing the logistics sector from the upside down, saving businesses time and money through streamlining the supply chain, and making it possible to outperform competitors and raise an organization's image. Thus, digital technologies in logistics provide the industry with sustainable success.
Andersen is fully-prepared to support the successful modernization of your organizations. We engineer versatile digital solutions for logistics, e.g., systems for managing warehouses, orders, inventories, and transport. Our talent pool has completed 45 projects for businesses around the globe: FedEx Ground, Nexxiot, Shypple, and others.